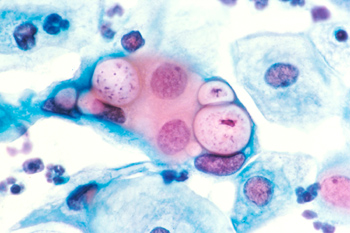
Chlamydia as seen under the microscope. courtesy wiki
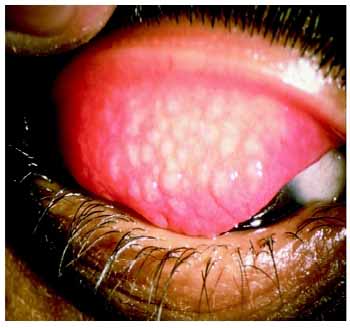
Chlamydia eye infection also called as Trachoma.
Chlamydia
Transmission to other people -
By having unprotected vaginal, anal or oral sex with someone who is infected.
From a mother to her baby during vaginal childbirth.
By transferring the infection on fingers from the genitals to the eyes.Diagnosis -
This is usually done by a doctor or a registered nurse trained in the examination of these patients.
An examination will be done of a patient’s genital area.
A urine sample may be taken.
Samples will be taken from any possibly infected areas, using a cotton wool or spongy swab.
Women will usually be given an internal pelvic examination, similar to a smear test, where a swab sample is taken from the cervix.
Men will be given an external examination of their testicles to check that these are healthy.
Treatment -
A course of antibiotics prescribed by physician. There are several antibiotics including Azithromycin, Doxycycline, Tetracyline, Erythromycin.
Treatment must not be interrupted once a course of antibiotics has been started; otherwise it may be necessary to start again from the beginning.
The infected patient should not have penetrative sex until treatment has finished and the doctor has confirmed they no longer have chlamydia by re-testing.
Follow-up
it is important that the patient returns for a check-up once the treatment has been completed to make sure they are well and have no recurring infection.
Prevention-
Treating STDs early can prevent PID. Women who are told they have an STD and are treated for it should notify all of their recent sex partners (sex partners within the preceding 60 days) so they can see a health care provider and be evaluated for STDs. Sexual activity should not resume until all sex partners have been examined and, if necessary, treated.